Data Types in C
A data type specifies the type of data that a variable can store such as integer, floating, character, etc.
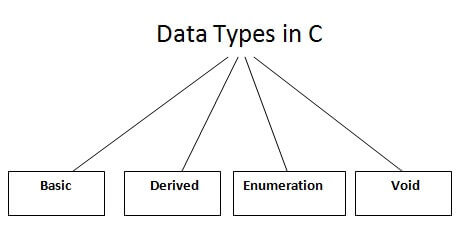
There are the following data types in C language.
| Types | Data Types |
|---|---|
| Basic Data Type | int, char, float, double |
| Derived Data Type | array, pointer, structure, union |
| Enumeration Data Type | enum |
| Void Data Type | void |
The basic data types are integer-based and floating-point based. C language supports both signed and unsigned literals.
The memory size of the basic data types may change according to 32 or 64-bit operating system.
Let's see the basic data types. Its size is given according to 32-bit architecture.
| Data Types | Memory Size | Range |
|---|---|---|
| char | 1 byte | −128 to 127 |
| signed char | 1 byte | −128 to 127 |
| unsigned char | 1 byte | 0 to 255 |
| short | 2 byte | −32,768 to 32,767 |
| signed short | 2 byte | −32,768 to 32,767 |
| unsigned short | 2 byte | 0 to 65,535 |
| int | 2 byte | −32,768 to 32,767 |
| signed int | 2 byte | −32,768 to 32,767 |
| unsigned int | 2 byte | 0 to 65,535 |
| short int | 2 byte | −32,768 to 32,767 |
| signed short int | 2 byte | −32,768 to 32,767 |
| unsigned short int | 2 byte | 0 to 65,535 |
| long int | 4 byte | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 |
| signed long int | 4 byte | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 |
| unsigned long int | 4 byte | 0 to 4,294,967,295 |
| float | 4 byte | |
| double | 8 byte | |
| long double | 10 byte |




0 comments:
Post a Comment